PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with good dielectric properties. This is especially true at high radio frequencies, making it eminently suitable for use as an insulator in cables and connector assemblies and as a material for printed circuit boards. Combined with its high melting temperature this makes it the material of choice as a high performance substitute for the weaker and more meltable polyethylene that is commonly used in low-cost applications.
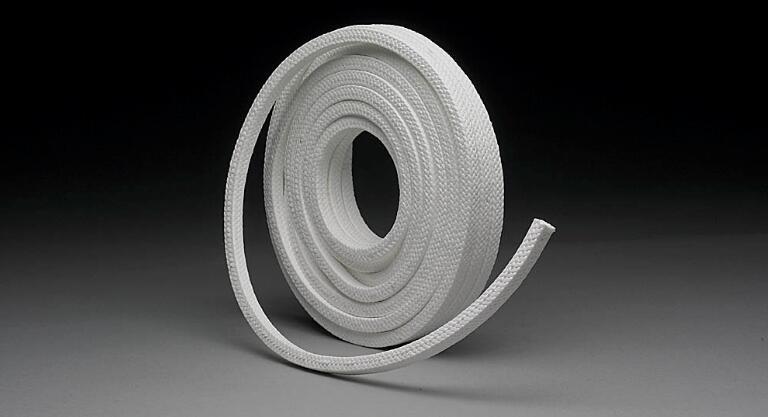

PTFE fiber is a chemically resistant material. It is used in woven form in certain pump packings as well as in nonwoven form in hot gas bag filters for industries with corrosive exhausts.
Because PTFE is relatively insoluble and has a very high melting point, PTFE fibers can not be fashioned from conventional melt or solution spinning. Instead they are made by combining particles of PTFE with cellulose, forming fibers of the cellulose and then sintering the PTFE particles (and charring the cellulose). The remnant char gives the fiber a brown color. It can be bleached white, although this reduces the strength.
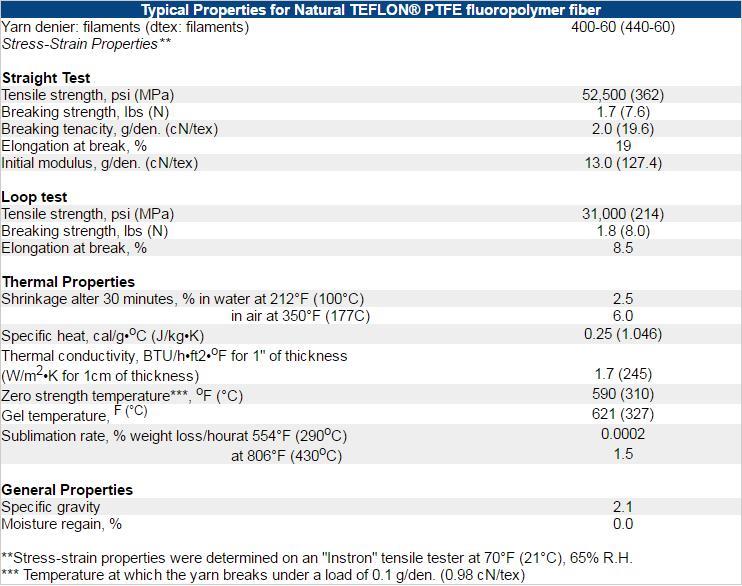
A summary of the stress-strain and gross properties for unbleached polymer® PTFE Fiber is shown in the table below.
Post time: Jan-10-2020

